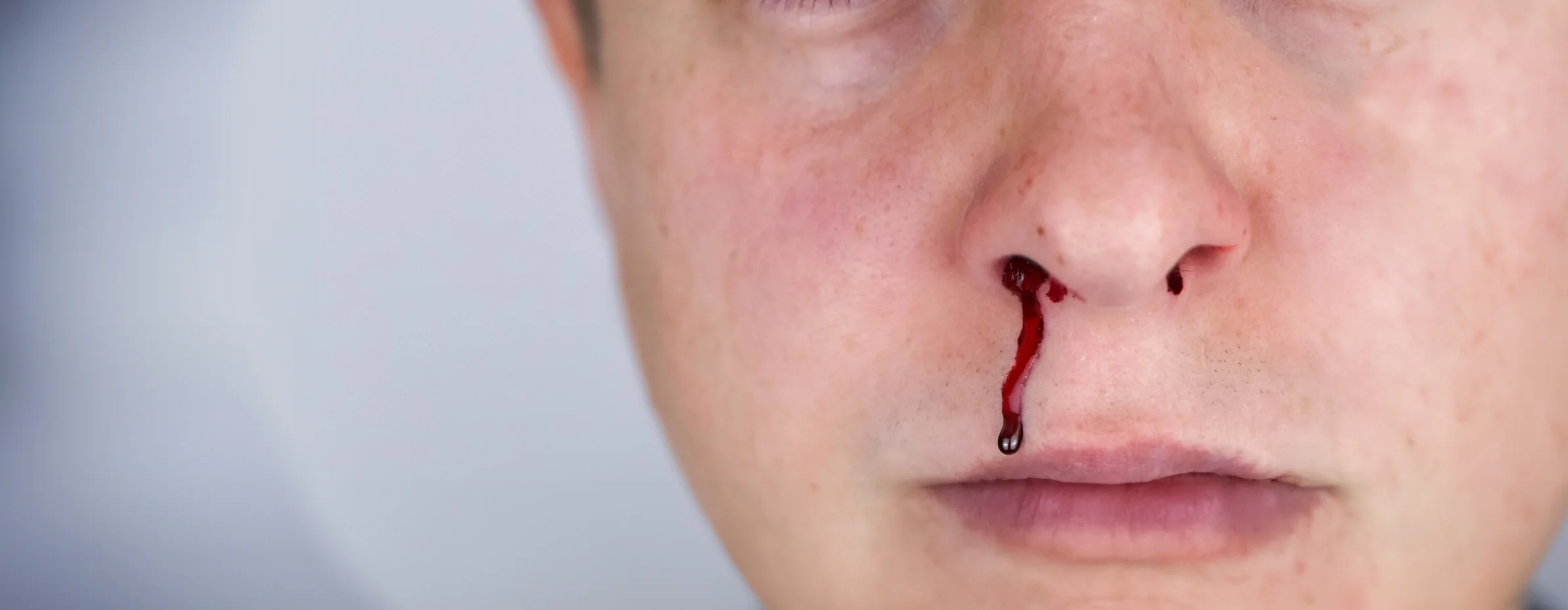
Congenital coagulation disorders represent a group of hereditary haemorrhagic pathologies caused by deficiencies in coagulation factors. Among the recurring symptoms, nosebleeds (epistaxis) are common and can be particularly debilitating for patients. This article aims to detail the main congenital coagulation disorders and provide practical recommendations for managing bleeds, both nasal and minor everyday wounds, highlighting the use of the BleedCEASE / NasalCEASE products.
The Main Congenital Coagulation Disorders
- Hemophilia A and B:
- Hemophilia A: Deficiency in factor VIII.
- Hemophilia B: Deficiency in factor IX.
- Symptoms: Prolonged bleeding after injuries, hematomas, spontaneous bleeding in joints and muscles.
- Prevalence: Hemophilia A (1 in 5000 male births), Hemophilia B (1 in 25000 male births).
- Von Willebrand Disease:
- Quantitative or qualitative deficiency in von Willebrand factor.
- Symptoms: Mucosal bleeding (epistaxis, gingival bleeding), heavy menstrual bleeding in women, postoperative hemorrhages.
- Prevalence: 1% of the global population.
- Factor XI Deficiency:
- Symptoms: Moderate to severe bleeding after surgery or injury, heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Prevalence: More common in Ashkenazi Jews (8%).
- Other Rare Deficiencies: Factors II, V, VII, X, XII, XIII:
- Symptoms: Vary depending on the deficient factor but generally include prolonged bleeding after injuries or surgical interventions.
- Management of Nosebleeds (Epistaxis)
- Nosebleeds in patients with coagulation disorders can be frequent and require a specific approach. Immediate and effective management is crucial to prevent significant blood loss.
- Recommendations:
- Compression: Pinch the nostrils for 10 to 15 minutes while keeping the head slightly tilted forward to avoid swallowing blood.
- Use of BleedCEASE/NasalCEASE packing :
- Description: BleedCEASE/NasalCEASE haemostatic nasal packing is made of calcium alginate, a natural product, extracted from seaweeds, that promotes coagulation.
- Method: Gently insert the packing into the bleeding nostril and keep it in place until the bleeding stops. The packing will jellify on the surface to allow a gentle, non-sticking removal after maximum 30 mn.
- Management of Minor Wounds
- Small cuts and abrasions are common and can also pose a significant problem for patients with coagulation disorders. BleedCEASE/NasalCEASE is the product suitable for these situations.
- Conclusion
- Managing bleeding in patients with congenital coagulation disorders requires specific knowledge and appropriate tools. The use of products like BleedCEASE/NasalCEASE, , is particularly effective for managing nasal bleeds and minor everyday wounds. A proactive and well-informed approach can significantly improve the quality of life for these patients.
- References
- National Hemophilia Foundation. Understanding Inherited Bleeding Disorders. https ://www.hemophilia.org/ 2. World Federation of Hemophilia. Guidelines for the Management of Hemophilia, 3rd edition. https://www.wfh.org/en/resources
- Mayo Clinic. Von Willebrand Disease. https://www.mayoclinic.org/
- Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Management of bleeding episodes in patients with inherited bleeding disorders: a clinical practice guideline.
NasalCEASE® and BleedCEASE® provide the easy to use answer
For treating minor nosebleeds and minor bleeding from topical cuts
Managing Bleeding in Patients on Anticoagulant Therapy
One of the most common and troublesome side effects reported by patients on anticoagulant therapy is the increased tendency to experience nosebleeds (epistaxis) and prolonged bleeding from minor cuts and abrasions. These bleeding episodes can be not only physically uncomfortable but also significantly disruptive to daily life. We will discuss the importance of managing these bleeding complications and provide practical recommendations for patients, emphasizing the use of BleedCEASE/NasalCEASE products to effectively control bleeding.
The Importance of Anticoagulant Therapy
Anticoagulant therapy is essential for many patients to prevent blood clots that can lead to stroke, myocardial infarction, and other serious conditions. VKAs, such as warfarin, and DOACs, such as apixaban and rivaroxaban, work by interfering with the blood’s ability to clot. While these medications are highly effective, their mechanism of action inherently increases the risk of bleeding.
Bleeding Complications: A Common Challenge
Patients on anticoagulant therapy often experience bleeding complications, ranging from minor inconveniences to severe medical emergencies. Among these, nosebleeds and prolonged bleeding from minor injuries are particularly common. These issues arise because anticoagulants thin the blood, making it more difficult for the body to form clots and stop bleeding.
The Impact of Uncontrolled Bleeding
While the primary goal of anticoagulant therapy is to protect cardiovascular health, uncontrolled bleeding can significantly impair a patient’s quality of life. Frequent nosebleeds can be distressing and socially embarrassing, while the inability to stop bleeding from minor cuts can make everyday activities challenging. In some cases, patients may become hesitant to engage in physical activities or may require medical intervention to manage their bleeding episodes.
Practical Solutions for Managing Bleeding
To address these challenges, I recommend a proactive approach to bleeding management for my patients on anticoagulant therapy. Specifically, I advise them to use BleedCEASE/NasaleCEASE products, which are designed to control bleeding effectively and safely.
BleedCEASE/NasalCEASE Nasal Packing for Nosebleeds
Product: BleedCEASE/NasalCEASE Nasal Packing
- Description: BleedCEASE/NasalCEASE Nasal Packing is made of calcium alginate, a natural hemostatic agent that promotes clot formation (bio-polymer extracted from seaweeds)
- Usage: Patients should gently insert the nasal packing into the bleeding nostril and leave it in place until the bleeding stops, but no more than 30mn. The packing helps to quickly control the bleeding and can be removed easily, without rebleeds, once the bleeding has ceased.
Small cuts and abrasions are common and can also pose a significant problem for these patients . BleedCEASE/NasalCEASE is the product suitable for these situations
Conclusion
While anticoagulant therapy is indispensable for the prevention of serious cardiovascular events, it is crucial to address the bleeding complications that patients may experience. Uncontrolled bleeding, whether from the nose or minor cuts, can be highly disruptive and distressing. By incorporating BleedCEASE/NasalCEASE products into their bleeding management strategy, patients can significantly reduce the impact of these side effects on their daily lives. This holistic approach not only ensures that the primary treatment goals are met but also enhances the overall quality of life for patients on anticoagulant therapy.
References
- National Hemophilia Foundation. Understanding Inherited Bleeding Disorders. https://www.hemophilia.org/
- World Federation of Hemophilia. Guidelines for the Management of Hemophilia, 3rd edition. https://www.wfh.org/en/resources
- Mayo Clinic. Von Willebrand Disease. https://www.mayoclinic.org/
- Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Management of bleeding episodes in patients with inherited bleeding disorders: a clinical practice guideline.
- American College of Cardiology. Management of Patients on Oral Anticoagulants. https://www.acc.org/
- International Journal of Cardiology. Practical considerations in the management of patients on anticoagulants. https://www.journalofcardiology.com/